Diverse Lark Species: Characteristics and Habitats


Intro
Birds have captured human fascination for ages. Among them, larks stand out as unique and captivating with their melodic songs and diverse species. This article aims to uncover their remarkable variety, examining the distinctive traits, behaviors, and habitats of larks. With many species spanning continents, understanding larks deepens our appreciation for their place in the ecosystem and helps us recognize the importance of conservation efforts.
As we venture deeper, we’ll also touch on their ecological roles, the relationship they share with their environment, and their cultural significance, weaving a narrative that showcases the importance of preserving these remarkable avian inhabitants.
Prolusion to Lark Species
Larks are remarkable creatures within the avian world, captivating bird enthusiasts and researchers alike with their unique characteristics and behaviors. Understanding larks is not just about appreciating their aesthetic appeal; it's about unraveling the significance they hold in our ecosystems and their ecological niches. By delving into the intricacies of various lark species, we can gain insights into their adaptations, challenges, and the fundamental roles they play within their environments. This exploration emphasizes the urgent need for conservation efforts aimed at preserving their habitats and, by extension, our natural world.
Significance of Larks in Avian Studies
Larks represent fascinating subjects in avian research, illustrating a spectrum of adaptations that showcase the resilience of bird species. Their diverse vocalization patterns serve as crucial components in understanding their communication methods, which vary from species to species. Whether it’s the melodious song of the Skylark or the distinctive calls of the Crested Lark, these vocalizations not only draw researchers' attention but also reveal much about social structures within lark populations.
Moreover, studying larks sheds light on evolutionary processes. Their adaptations to various habitats highlight how environmental pressures influence morphological and behavioral traits—a compelling narrative for evolutionary biology students and professionals.
For aspiring bird watchers and pet bird owners, recognizing signs of lark calls or behaviors can enhance appreciation and connection to local wildlife. When individuals understand these aspects, they can more effectively contribute to the dialogue surrounding avian conservation, equipping themselves with knowledge to advocate for informed practices in bird care and habitat preservation.
Overview of Their Distribution
Larks are found across diverse regions, with their presence spanning from open grasslands to deserts. This wide distribution showcases their adaptability. The Alaudidae family, which includes more than 90 recognized species, occupies various continents, primarily across Europe, Asia, and Africa, with selective species even inhabiting parts of North America.
For instance, the Eurasian Skylark thrives in temperate grasslands and urban areas, reflecting its versatility. Conversely, the Hume’s Lark is primarily endemic to the mountainous regions of the Himalayas, exhibiting a unique adaptation to high-altitude environments. This geographic variation provides an opportunity for studies in biogeography and evolution.
The fluctuations in habitat can also serve as indicators of climate change and ecological shifts, influencing bird population dynamics. Regions that were once havens for lark populations may now see declines due to habitat destruction or climate-related changes. By identifying and mapping where various lark species thrive, researchers can implement strategic conservation efforts tailored to their specific environments.
"Larks tell us about the health of their ecosystems; their presence or absence can signal broader environmental issues."
Taxonomy and Classification
Taxonomy and classification is a crucial aspect of studying larks. By understanding their systematic framework, we can better appreciate the diversity of these fascinating birds. Taxonomy helps in grouping organisms based on shared characteristics, guiding ornithologists in identifying species and understanding their relationships to others within the Avian world. For those keen on pet ownership or breeding, grasping the nuances of lark taxonomy can assist in making informed decisions regarding species selection and care requirements.
Classification is more than names and categories; it represents a hierarchical system ranging from broad categories like family to specific species. This influences habitat preferences, behavioral traits, and even conservation efforts. By studying the taxonomy of larks, one can discern how certain environmental factors have sculpted distinct groups over time.
Family Alaudidae: An Overview
The family Alaudidae, commonly known as larks, comprises over 90 species spread across various habitats worldwide. This family is characterized by its variable size, with some larks quite small, while others present larger frames. Typically, larks exhibit a rounded body with a distinctive long tail and a charmingly melodious song that has captivated many a bird-watcher.
Unique Traits and Distribution
The lark's melodious calls serve purpose beyond mere beauty; they play a key role in communication, especially during the breeding season. Alaudids are predominantly terrestrial birds, often found hopping along the ground in search of insects and seeds. Some species, like the Eurasian skylark, are known for their remarkable aerial displays and singing while in flight.
Larks prefer open environments, favoring regions like grasslands and steppes where their cryptic plumage provides camouflage from predators. This adaptability makes them a common sight in the plains of Africa and the grasslands of North America.
Key Genera within Larks
Within family Alaudidae, several genera stand out. The genus Alauda includes the well-known Eurasian Skylark. This species is often lauded for its impressive vocal abilities and striking display during mating rituals. On the other hand, the genus Calandrella encompasses several smaller lark species, commonly found in more arid environments.
- Alauda
- Calandrella
- The Eurasian Skylark (Alauda arvensis)
- Common Skylark
- Lesser Short-toed Lark
- Greater Short-toed Lark
Each genera showcases distinctive traits, reflecting adaptations to their environments and lifestyles. Understanding these genera not only enriches our appreciation for larks but can also provide insights into conservation strategies tailored to specific groups.
"Taxonomy is like a tree, with each branch representing a different lineage, guiding us through the rich diversity of life."
In summary, the study of taxonomy and classification serves as a gateway to comprehending the intricate world of larks, their behaviors, and their ecological significance. This critical knowledge helps bird enthusiasts and scientific researchers promote better conservation practices, ensuring that we can continue to enjoy the songs and beauty of these avian gems.
Physical Characteristics of Larks
Understanding the physical characteristics of larks is more than a scientific interest; it dives into the very essence of what makes these birds unique. The nuances in their size, morphology, and coloration not only serve functional purposes in their habitats but also contribute deeply to their adaptability and survival strategies. For pet bird owners and aspiring bird parents, recognizing these traits can provide valuable insights into lark behavior, needs, and care requirements. Let's break down the specifics.
Size and Morphology
Larks exhibit a range of sizes that adds to the richness of their species diversity. Generally, they vary from about 12 to 18 centimeters in length, with a average wingspan of around 25 centimeters, which is crucial for their foraging and migratory habits. Small yet sturdy, their body shapes can be compact or elongated, with some species sporting particular adaptations that help them thrive in specific environments.
Notably, many larks possess strong legs that facilitate ground foraging, while their feet are keenly adapted to the habitats they inhabit. For instance, the Horned Lark tends to have shorter legs, which aid in moving through dense grasses, while the Eurasian Skylark features slightly longer legs, accommodating its penchant for more open space.
The morphological features of larks—such as their beaks—are equally important. Their beaks, generally conical, are perfectly designed for their diet, which primarily includes seeds and insects. The design allows for efficient feeding, whether they are pecking at the ground or taking advantage of food found in shrubs. This adaptability showcases their evolutionary responses to dietary demands and environmental challenges.
Coloration and Plumage Patterns
When it comes to coloration and plumage patterns, larks don’t shy away from showing off their unique styles. This aspect of their physical makeup serves several ecological and social functions. The palette of colors ranges from browns and greens to more vibrant shades, providing essential camouflage in their environments.
For example, the Sand Lark often sports a sandy brown coloration, which blends seamlessly with the arid landscapes it inhabits. On the other hand, larks like the Calandra Lark have a more mottled appearance, which helps them evade predators by breaking up their silhouette against the grasslands.
Moreover, their plumage is not merely for show; it plays a significant role in courtship rituals. Many male larks flaunt more vibrant plumage during breeding season to attract potential mates. The patterns and colors can signal health and vitality, thus influencing mating success.
"In lark species, color variation often correlates directly with habitat needs and mating displays, highlighting the intricate relationship between a bird’s environment and its physical traits."


Habitat Preferences
Understanding the habitat preferences of larks is essential for appreciating their adaptability and survival strategies. Larks, belonging to the family Alaudidae, are widely distributed across various types of environments. Their choice of habitat often reflects their evolutionary adaptations, which make them remarkably resilient.
Grasslands and Open Countryside
Larks thrive in grasslands and open countryside, ecosystems that offer ample space for foraging, nesting, and displaying their vibrant behaviors. These settings are typically characterized by low vegetation, which provides necessary cover and breeding grounds. The soil in these areas is often rich in seeds and invertebrates, forming the backbone of their diet.
In many instances, these open spaces allow for their famous aerial displays during courtship. For example, the Sky Lark often flies high into the air, singing as it ascends, before gliding down gracefully. This behavior not only attracts mates but also demonstrates territorial claims.
Additionally, the vastness of grasslands is crucial for the larks’ foraging habits. The birds scoot through the ground, picking up seeds and insects. They often utilize their agility, adapting their movement to the contours of the land. This enables them to evade potential predators while searching for food, showcasing a remarkable adaptation to their habitat.
Importantly, changes in land use, such as agriculture and urban encroachment, pose threats to these environments. As agricultural fields replace natural grasslands, it can lead to a significant decline in lark populations, making the preservation of these habitats all the more crucial.
Urban Adaptations in Certain Species
Interestingly, some lark species are not confined to rural environments and have adapted surprisingly well to urban settings. This shift has opened new avenues for their survival, highlighting their remarkable flexibility. In cities, you might find species like the Crested Lark confidently inhabiting parks and gardens, where they can hunt for crumbs and seeds.
Urban environments have their own unique resources, enabling these larks to adjust their foraging strategies. Instead of exclusively relying on grasslands for insects and seeds, they often capitalize on human activity, scavenging in public areas and benefiting from discarded food. Their ability to thrive in these diverse conditions is a testament to larks’ resilience and adaptability.
However, life in urban areas is not without challenges. Noise pollution can interfere with their communication methods, while habitat fragmentation can limit their movement and accessibility to nesting sites. Ultimately, while some lark species have become urban dwellers, the delicate balance between adaptation and survival remains precarious.
"Larks exhibit an impressive capacity to adapt to their habitats, whether it be the open skies of grasslands or the bustling streets of cities. Their behaviors reflect their resilience and resourcefulness."
In summary, the habitat preferences of larks span from expansive grasslands to the heart of urban landscapes. This diversity is reflected in their foraging habits, nesting behavior, and adaptability to changing environments, making them a fascinating subject of study for bird enthusiasts and researchers alike.
Diet and Feeding Habits
Understanding the diet and feeding habits of larks is crucial to appreciating their adaptability and ecological roles. Different lark species showcase a remarkable variety in what, and how, they eat, shaped by their specific environments. These feeding behaviors not only influence their survival but also play a significant part in the health of the ecosystems they inhabit. For those interested in keeping larks as pet birds or breeding them, recognizing their dietary needs becomes paramount.
Primary Diet Composition
The diet of larks predominantly consists of seeds and insects. This blend of plant and animal matter provides the necessary nutrients for growth and reproduction. While the particular composition can vary based on the species and geographical location, here are some common elements:
- Seeds: Various lark species favor different types of seeds. For instance, the horned lark often prefers the seeds of grasses and herbs. Seeds are typically collected from the ground, demonstrating larks' proficiency as ground foragers.
- Insects and Larvae: Insects serve as a vital protein source, especially during breeding seasons. Species like the skylark notably consume a variety of insects, which supply the essential amino acids needed for chick development.
- Green Vegetation: Occasionally, larks may eat leaves and stems, especially in times of scarcity. This practice highlights their opportunistic feeding nature, ensuring they can adapt when food sources fluctuate.
The balance of these diet components is important, affecting larks' energy levels, growth rates, and reproductive success. As any bird owner or breeder will attest, aligning a pet bird’s diet with natural habits fosters overall well-being.
Foraging Strategies
Larks employ several foraging strategies to locate food effectively, adapting their techniques to suit available resources. Some of these strategies include:
- Ground Foraging: Larks are adept at searching for food on the ground. They often run and hop, using their keen eyesight to spot seeds or insects hidden under grass or soil.
- Aerial Foraging: Certain species, like the sky lark, exhibit aerial foraging. They soar into the air to catch insects mid-flight, displaying remarkable agility and skill.
- Mixed Feeding: Many larks vary their feeding methods based on habitat. They might combine ground foraging with climbing low shrubs to reach seeds or fruits, showcasing their versatility.
"Larks demonstrate incredible adaptability in how they source their food, ensuring their survival across various environments."
In summary, the dietary habits of larks are as diverse as the species themselves. Recognizing the specific dietary needs and foraging strategies based on their natural behaviors can significantly enhance the care and environment provided by bird enthusiasts, be they pet owners or breeders.
Behavioral Traits
Behavioral traits of larks provide vital insights into their ecological roles as well as their adaptability to different environments. Understanding how these birds communicate, mate, and exhibit social behaviors can help in recognizing their needs and the challenges they face in the wild. These behaviors are crucial not just for their survival but also for the ecosystems they inhabit. Additionally, they may offer hints to pet bird owners and aspiring breeders about what to look for when selecting larks for companionship or breeding purposes.
Vocalization and Communication
One of the most captivating aspects of lark behavior is their vocalization. These birds are known for their melodious songs that fill the air, especially during the breeding season. The songs serve multiple purposes:
- Territorial Claims: Males often sing to stake their claims in a territory, warning other males to steer clear. This helps reduce physical confrontations which could be detrimental.
- Attracting Mates: A well-performed song can significantly enhance a male’s appeal to potential mates. Females are often selective, gravitating towards males with complex and varied calls.
- Social Interaction: Beyond mating, vocalizations facilitate communication within flocks. Different calls can signal danger or coordinate movements when foraging.
It’s fascinating how regional dialects emerge among lark populations, much like human languages, emphasizing the cultural aspect of their communication. According to a study published on britannica.com, some lark species possess unique calls that can vary from region to region, indicating a deep connection between bird behavior and environmental factors.
"The song of the lark is not just a melody; it’s a dialogue with the world, rich with meaning and purpose."
Mating Rituals and Courtship
When it comes to mating rituals, larks have developed intricate displays that are as fascinating as their songs. The courtship process often involves a combination of vocalizations, flight displays, and even physical prompts:
- Display Flights: Males engage in impressive airborne displays, soaring high into the sky and then diving spectacularly. This not only showcases their agility but also allows them to demonstrate their fitness to potential mates.
- Duets: In some species, male and female larks perform duets, an engaging display of synchronized singing that is both charming and efficient in showcasing their bond.
- Territorial Displays: During the courtship phase, males may also perform various physical displays on the ground. They can fluff their feathers or bow, signaling their readiness to mate.
These behaviors highlight the complex social structures of larks. For pet bird owners, observing courtship displays can provide insight into their well-being and help mimic an environment that allows for natural behaviors. It can also inform breeders on the best practices for pairing larks, leading to healthier offspring.
In summary, the behavioral traits of larks not only enrich our understanding of their ecological roles but also offer practical knowledge for those engaging with these birds in captivity. The melodious songs and elaborate courtship rituals provide a glimpse into their world that is both mesmerizing and essential for their survival.
Breeding and Reproductive Strategies
Breeding and reproductive strategies in larks are vital for understanding their survival and adaptation in the wild. These strategies aren't just about increasing the number of birds; they ensure that the next generation possesses the traits needed to thrive in their specific environments. The variety of breeding habits among lark species reflects their diverse ecological niches and preferences, which can be quite complex.
One noteworthy aspect is the timing of breeding, which often aligns with local climatic conditions. For example, many larks breed in the spring when food resources are abundant. In regions where rainfall can vary, larks may time their nesting to capitalize on peak insect populations, ensuring their chicks have ample food. This reflects a keen understanding of their local ecosystems, showcasing their ability to adapt and thrive.
Furthermore, lark mating rituals can be quite elaborate and are crucial for securing healthy offspring. Males often engage in aerial displays showcasing their plumage and vocal abilities. A striking performance can attract females, leading to successful pair bonding. These displays vary among species; however, the underlying goal remains constant: to demonstrate fitness and genetic quality.
"In nature, adaptability is often the key to survival; larks exemplify this through their varied breeding strategies."


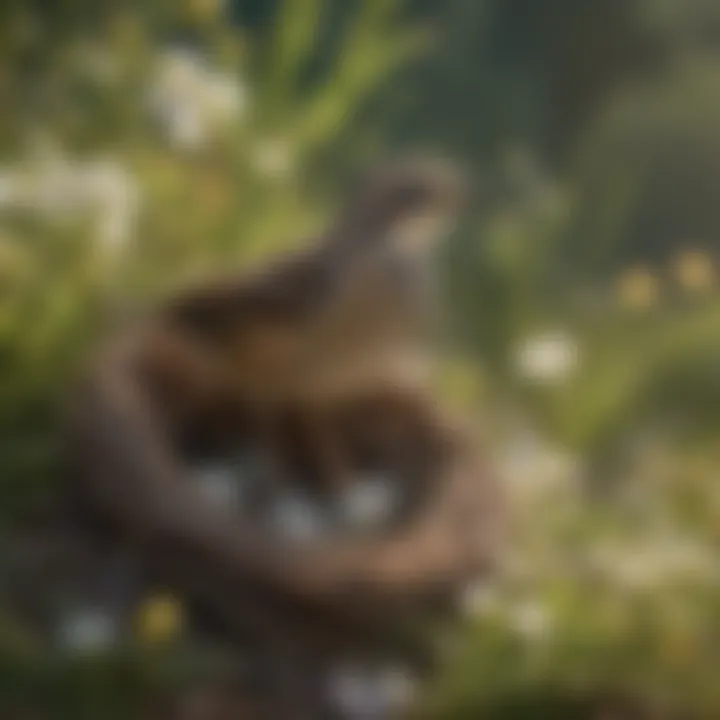
Nesting Habits
Larks exhibit fascinating nesting behaviors that differ widely among species. Most larks prefer ground nesting, which makes them vulnerable but also helps them blend into their surroundings. Their nests are often strategically placed in long grasses or other dense vegetation, providing some measure of concealment from predators.
The nest construction usually involves materials readily available in their habitat, such as dried grass, feathers, and sometimes even bits of discarded human materials. This resourcefulness reflects their keenness for survival. Larks also construct their nests relatively close to each other, especially in areas of high population density, which can lead to vibrant breeding colonies supporting one another.
In colder climates, some species adapt by using their nests as insulation during chilly nights, ensuring that both eggs and chicks are kept warm. The choice of nesting site and materials further highlights how larks have evolved to enhance their reproductive success in varying environmental contexts.
Chick Development and Care
Once the eggs hatch, the joy of parenthood extends into the chick development phase. Lark parents are notably attentive, contributing to the nurturing of their young. Typically, both male and female participate in feeding and protecting the chicks, which aids in ensuring a higher survival rate.
Chicks are born altricial, meaning they are underdeveloped and rely heavily on their parents. Initially, they are featherless and blind, demanding constant care. During the first few weeks, parents bring a steady diet of insects and seeds, which are crucial for the rapid growth of the chicks.
As the chicks grow, they undergo significant physiological changes, including the development of feathers and the ability to regulate body temperature. By about two weeks, they are starting to venture out of the nest under parental supervision, exploring their surroundings while still being sheltered and fed by their parents. This careful nurturing process is a direct reflection of the strong bond between lark parents and their offspring.
In summary, the breeding and reproductive strategies of larks encompass various elements that highlight their remarkable ability to adapt. From nesting habits suited to their environment to devoted parental care, these traits ensure the continuity and flourishing of lark populations.
Geographical Distribution
Understanding the geographical distribution of larks is essential for several reasons, as it opens our eyes to the vast tapestry of their habitats and behaviors. The locations where these birds thrive offer clues to their adaptability and survival strategies. Furthermore, these distributions highlight the ecological contexts in which larks operate, helping us appreciate the nuanced relationships they have with their environments.
Larks are typically found in regions characterized by open landscapes such as grasslands, savannas, deserts, and agricultural areas. Their preference for wide, unobstructed spaces allows them to perform their characteristic songs and foraging behaviors effectively. Notably, larks are not just confined to one corner of the globe but stretched across continents, showcasing a fascinating array of adaptations to different ecological niches. This diversity is not merely a statistical curiosity; it has real-world implications for conservation, as changes in land use and climate can significantly impact these populations.
Regions of High Diversity
When we talk about regions of high diversity for lark species, several key areas come to mind. For instance, the vast steppe regions of Central Asia stand out as a hotspot. Here, you will find a variety of lark species, including the exquisite Sky Lark and the striking Eurasian Skylark. These species thrive despite the harsh conditions due to their specialized adaptations.
Another hotspot worth mentioning is southern Africa, particularly the Kalahari Desert areas. Larks like the Rufous-Naped Lark have adapted to the arid conditions and scarce vegetation. Their survival in such extreme environments is a testament to their resilience and evolutionary versatility.
These regions not only support a rich diversity of lark species but also serve as essential research locations for ornithologists and conservationists alike. Understanding where these birds flourish can lead to more effective strategies for habitat preservation.
Migratory Patterns of Select Species
Many lark species showcase impressive migratory patterns, exhibiting behaviors that highlight their adaptability. For instance, the Thick-Billed Lark has been known to undertake extensive migrations seasonally, moving from breeding areas in Africa to the richer feeding grounds found in Europe during different times of the year.
Moreover, Horned Larks provide another fascinating study in migration. These birds often shift their range based on the changing seasons, retreating northward in the spring and returning south as winter arrives. What’s striking is how their migratory routes can be influenced by factors like food availability and nesting environment—not just pure instinct.
Understanding these migratory trends sheds light on not just the biology of larks, but also broader environmental changes. Global shifts in climate may alter these migration patterns, impacting not just the larks themselves but the ecosystems as a whole. Conservation efforts must take these patterns into account to ensure sustainable habitats for future generations of larks and the diverse ecosystems they inhabit.
Ecological Importance of Larks
The ecological significance of larks stretches far beyond their melodious calls and pleasing aesthetics. These birds play a vital role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems in which they thrive. By examining the role of larks, we can uncover how their behavior and dietary preferences intricately weave them into the fabric of their environments. Their interactions influence not just their immediate surroundings, but also the broader ecological dynamics.
Larks contribute to the health of grasslands and open landscapes, areas where they are predominantly found. They help control insect populations, serving as a natural form of pest management that benefits agriculture and crop production. Additionally, their foraging habits, which primarily involve scratching the soil for seeds and invertebrates, promote soil aeration and nutrient cycling, crucial processes for sustaining plant life.
Moreover, larks often serve as a food source for various predators, establishing important food web connections. By understanding their ecological roles, the broader implications of their population fluctuations become evident. Loss of lark populations can have cascading effects on both flora and fauna in their habitats, leading to declines in plant diversity and an imbalance in predator-prey relationships.
"The presence of larks in an ecosystem is an indicator of its overall health. Their decline may signal potential threats to habitat integrity."
Role in Ecosystem Dynamics
Larks significantly impact the ecosystems they inhabit. As foragers, they interact with their environment in multiple ways. Their propensity for seed and insect consumption means they play a critical part in maintaining healthy plant communities while also providing sustenance to higher trophic levels.
- Nutrient Cycling: Through their feeding habits, larks contribute to nutrient recycling as they break down organic matter and redistribute seeds across their territory.
- Pollination: In some cases, larks aid in pollination while seeking nectar from flowering plants, although they do not possess the specialized adaptations seen in traditional pollinators.
- Indicator Species: Because they are sensitive to environmental changes, larks can serve as bioindicators, alerting researchers and conservationists to shifts in habitat quality and ecosystem health.
Understanding these dynamics helps inform conservation efforts and highlights the interconnectedness of lark populations with their larger ecological communities.
Impact on Prey and Predator Relationships
The interactions between larks and their predators are pivotal in maintaining ecological harmony. As prey species, larks themselves are integral to the diets of several larger birds of prey, mammals, and reptiles. Their presence or absence can significantly alter the behaviors and populations of these predators.
- Predator Population Control: Larks can influence predator populations by serving as a reliable food source, impacting their breeding success and territory sizes.
- Creating Trophic Cascades: Changes in lark populations may result in trophic cascades that can lead to overpopulation or decline of certain species, therefore altering the ecological balance.
- If lark numbers dwindle, predators may seek alternate prey, putting additional pressure on different species.
- Conversely, if lark populations thrive, they can enhance the fitness of their predators, creating robust food webs.
Considering these relationships underscores the complexity of ecological systems and the crucial role that even small bird species like larks play in sustaining ecological integrity. Monitoring and protecting lark habitats can thus have broader implications for conserving numerous interdependent species.
Conservation Status and Challenges
Lark species play a crucial role in their ecosystems, yet their conservation status presents significant challenges. Understanding these challenges is paramount as it informs both conservation efforts and the ecological balance these birds help maintain. Examining the factors threatening lark populations sheds light on what can be done to preserve their diversity. It highlights the need for sustained conservation initiatives that target the specific conditions impacting these birds.
Threats Facing Lark Populations
Various threats are contributing to the decline of lark populations around the world. Some key elements include:
- Habitat Loss: One of the most immediate threats larks face is habitat destruction. Urban expansion, agricultural development, and industrialization are knocking down grasslands and open spaces that larks depend on for feeding and breeding. This shift not only reduces the available nesting sites but also increases competition for limited resources.
- Agricultural Practices: Intensive farming methods, especially the use of pesticides and herbicides, pose significant risks to lark populations. These chemicals may kill off insects, which are crucial for lark diets during their breeding season. Moreover, monoculture farming reduces biodiversity in the areas where larks might forage.
- Climate Change: As the climate changes, larks may struggle to adapt to shifting weather patterns and changing ecosystems. Altered precipitation patterns can directly impact the availability of their natural habitats. Additionally, extreme weather events can lead to higher mortality during critical nesting periods.
In summary, the intertwined threads of habitat loss, agricultural impact, and climate change present a formidable challenge for maintaining healthy lark populations.
Conservation Efforts and Initiatives

Despite the hurdles, there are ongoing efforts aimed at conserving lark populations across the globe. Conservation initiatives can be varied, reflecting both localized needs and global awareness. Some actions being taken include:
- Restoration Projects: Many organizations focus on habitat restoration, aiming to revive the grasslands larks thrive in. These projects typically involve replanting native flora and removing invasive species to encourage the natural ecosystem to rebound.
- Sustainable Farming Practices: Encouraging farmers to adopt more bird-friendly practices can make a significant difference. Techniques such as crop rotation, reduced pesticide use, and leaving natural hedgerows can create a more hospitable environment for larks and other wildlife.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Educating the public about the significance of larks and the challenges they face is essential. Campaigns can help promote community involvement in conservation activities, which in turn can create local advocates for lark preservation.
- Monitoring and Research: Continuous monitoring of lark populations aids in assessing the effectiveness of conservation strategies. Research helps in understanding the specific needs and behaviors of different lark species, informing tailored conservation practices.
Ultimately, a multifaceted approach combining habitat protection, sustainable practices, and community engagement is vital for reversing the trends affecting lark populations. The drive to engage a broader audience, including bird owners and aspiring bird enthusiasts, in conservation efforts can lead to sustainable success.
Larks in Culture and Folklore
Larks have long been entwined in the cultural fabric of various societies, symbolizing different concepts and inspiring countless works of art and literature. Their presence in folklore serves not only as a representation of nature but also as a mirror reflecting human emotions and aspirations. Understanding the cultural significance of larks reveals a deeper appreciation for these birds beyond their ecological roles.
Symbolism Across Different Societies
In many cultures, larks symbolize joy, freedom, and hope. Their melodious songs are often associated with the beauty of dawn, heralding a new day. This connection to renewal is seen in various traditions:
- Ancient Greece: For the Greeks, the lark was linked to Apollo, the god of music and poetry. Its song was seen as a divine blessing.
- Persian Poetry: In Persian literature, larks are often depicted as symbols of love. Their singing is believed to express the heart's longing, making them a fitting metaphor in romantic verses.
- Native American: Some tribes regard the lark as a messenger, carrying prayers to the heavens. Its call is believed to be a way of connecting the Earth to the spirit world.
This varied symbolism shows how larks serve as more than just creatures of flight; they become powerful cultural icons, embodying the values and beliefs pertinent to different people.
Larks in Art and Literature
Artists and writers across centuries have drawn inspiration from larks, translating their fleeting beauty and songs into various art forms. Here are some notable instances:
- Visual Arts: Renowned painters, like John James Audubon, have often highlighted larks in their works, capturing their natural grace and vibrant stages of life. Their depictions emphasize the serene beauty that larks contribute to landscapes.
- Literature: Classic poets, such as William Wordsworth, have celebrated the lark's morning song in their verses. In "To a Lark," he describes the bird soaring high, representing unfettered joy and elation. This poetic embrace encourages readers to almost hear the lark's tune resonating in their imaginations.
- Songs and Folk Tales: Across many cultures, larks appear in folk tales where they represent associated morals, such as honesty and perseverance. These stories often aim to convey deep lessons, resonating with the human experience.
"Larks are like threads weaving through the tapestries of human culture, reminding us of nature’s intricacies and our shared stories."
In closing, the cultural and folklore significance of larks enriches their narrative. They serve not merely as delightful avian singers in the wild but as profound symbols, echoing diverse human sentiments and thoughts set to flight.
Future Directions in Lark Research
Advancing the understanding of larks is vital for both conservation efforts and the appreciation of their ecological roles. Future directions in lark research emphasize the need to bridge gaps in knowledge, address pressing challenges, and harness innovative methodologies. As habitats continue to change and pressures from human activities mount, it's essential to keep a finger on the pulse of lark populations and their needs. While much has been learned, there's still a treasure trove of insights waiting to be uncovered.
Emerging Trends in Conservation Science
The realm of conservation science is rapidly evolving, and lark species could greatly benefit from some of these emerging trends. For instance,
- Genetic Research: Advancements in genetic research allow scientists to delve deeper into the genetic diversity of lark populations, revealing insights that could shape conservation strategies. Understanding the genetic makeup can help determine the resilience of species to environmental changes.
- Habitat Restoration Techniques: New approaches in habitat restoration are beginning to show promise for larks that rely on specific environments. Projects aimed at restoring grasslands and open spaces often consider the nesting habits and feeding preferences of these birds, creating tailored solutions.
- Climate Adaptation Strategies: Given the shifting climate, understanding how larks might adapt to new conditions is crucial. Researchers are exploring behavioral changes and geographic shifts, which can inform conservation actions.
- Technology Integration: The integration of technology into field studies has enhanced data collection greater than ever before. From drones mapping habitats to acoustic monitoring of calls, scientists now have tools to gather substantial amounts of data efficiently.
These trends not only advance the science of conservation but also provide an opportunity for better-informed, proactive measures in protecting lark populations.
Integrating Citizen Science in Lark Studies
One of the most engaging avenues for future lark research is the integration of citizen science. Harnessing the power of community involvement opens doors to a wealth of information. Pet bird owners, aspiring bird parents, and bird breeders can play a pivotal role in contributing to knowledge about larks and their habitats.
- Data Collection: Ordinary enthusiasts can track lark sightings and behaviors, essentially acting as citizen scientists. This data can be invaluable, particularly in regions where formal research is sparse.
- Public Awareness: Engaging the wider community increases awareness about lark species, their challenges, and the importance of habitat conservation. As more people become informed, the collective capacity to advocate for lark preservation grows.
- Collaborative Projects: Initiatives like local birding clubs or online platforms on Reddit can bring enthusiasts together to share findings and formulate strategies that benefit larks. These collaborative efforts often spark innovative ideas.
- Educational Opportunities: Workshops and presentations by lark researchers to local communities can excite enthusiasm for studying avian life. Education empowers citizens to contribute meaningfully.
"As we engage the community, we not only expand our understanding of larks but also build a network of advocates eager to protect these remarkable birds."
The future of lark research looks promising, especially when leveraging the enthusiasm of bird lovers who can contribute in ways that professional researchers alone cannot. With every observation made and data point collected, the entire field of lark study can move forward in leaps and bounds.
User Engagement and Community Involvement
In the context of avian studies, particularly concerning lark species, user engagement and community involvement serve as vital facets that bridge the gap between scientific research and public appreciation. While experts collect data, it is the collective efforts of enthusiasts and the general public that can amplify our understanding of these birds. The role of citizen science can’t be overstated; by providing platforms for everyday people to share their experiences and observations, we gather invaluable data that might be otherwise overlooked.
Contributing to Citizen Databases
Citizen databases have become a cornerstone in tracking lark populations and behaviors. Initiatives such as eBird, a project by the Cornell Lab of Ornithology, allow bird enthusiasts to contribute their sightings and observations. This information assists researchers in mapping migration patterns, assessing population health, and understanding habitat preferences. Contributions can range from simple checklists of species seen during a birdwatching outing to detailed notes on behavioral patterns observed in specific locales.
Moreover, participating in these databases not only enriches scientific knowledge but also fosters a sense of community among birdwatchers. The feedback loop created by sharing findings can lead to more focused research questions and efforts tailored toward conservation.
Sharing Observations and Findings
Sharing observations and findings is another pillar supporting lark studies. Online platforms such as Reddit and Facebook foster spaces for bird lovers to discuss their experiences with larks. Enthusiasts often share photographs, behavioral anecdotes, and even engage in discussions about the challenges they face when observing these species. The importance of this sharing cannot be underestimated; it cultivates an environment where knowledge flows freely.
Consider a bird parent who notices a peculiar behavior in their lark. By sharing this finding with an online community, it could spur discussions that lead to a broader understanding of lark behavior across different regions. This dissemination of information contributes significantly to the collective understanding of the species and can inform future research efforts.
"Every sighting, every note shared, adds to the tapestry of our understanding of these remarkable birds."
The End
In wrapping up our exploration of lark species, it's essential to underscore the significance of understanding both their diversity and the factors that affect their survival. These robust birds inhabit various ecosystems, each contributing to the intricate web of life around them. Examining larks not only offers insights into their unique adaptations and behaviors but also prompts a broader reflection on how we, as stewards of the environment, can influence their future.
Reflections on Lark Diversity
Diversity in lark species is a testament to nature’s ability to evolve and adapt. More than just a subject for ornithological study, larks embody ecological flexibility. With their varied habitats and behaviors, they serve as indicators of environmental health. By exploring the myriad species, one comes face-to-face with the beauty of nature's complexity. The way they adjust their song patterns in different habitats, or how their plumage varies across regions, reveals layers of evolutionary stories that have unfolded over millennia. Observing these birds in their natural environments can be utterly captivating. Every chirp and flit provides a glimpse into their intricate lives, highlighting how essential they are to the ecosystems they inhabit.
The multifaceted roles larks play—from seed dispersers to prey for larger species—underscore why preserving their diversity is paramount. Each species holds potential keys to understanding environmental interactions, providing a window into the past and a guide for the future. Larks are not just birds; they are part and parcel of the ecological narrative we all share.
The Importance of Habitat Preservation
Preserving habitats is crucial for larks and their fellow avian and terrestrial inhabitants. The threats of habitat loss, specifically due to urbanization and agricultural expansion, cannot be overstated. Larks thrive in open grasslands and fields, areas that are often first to go in the name of development. Protecting these environments is not just a matter of conserving larks; it’s about sustaining the entire ecological balance.
Several conservation initiatives are underway to secure vital habitats for these birds, emphasizing the need for land-use practices that protect open spaces and biodiversity. Local communities can play a pivotal role by advocating for wildlife-friendly landscapes.
- Create Bird-Friendly Spaces: Encouraging schools and parks to maintain areas of native grasslands can have significant positive impacts.
- Participate in Conservation: Organizations often rely on community involvement for tracking and monitoring bird populations and habitats.
- Incorporate Citizen Science: Engaging with citizen science projects can create a larger awareness of larks and their needs, thus fostering a greater commitment to habitat protection.
"The health of our planet can often be gauged by the flourishing of its wildlife, and larks serve as an important measure of biodiversity in their respective environments."
To sum it up, the vibrancy and significance of lark species illuminate the article’s core goal: to raise awareness about their rich diversity and highlight the necessity of safeguarding their habitats. As we reflect on our role in conserving these intriguing birds and their environments, it is clear that the fate of larks is intertwined with our own interactions with nature.















